by Blog | Mar 5, 2023 | Cybersecurity
No business wants to suffer a data breach. But unfortunately, in today’s environment, it’s difficult to completely avoid them. Approximately 83% of organizations have experienced more than one data breach. (IBM Security 2022 Cost of a Data Breach Report)
These breaches hurt businesses in many ways. First, there is the immediate cost of remediating the breach. Then, there are the lost productivity costs. You can add lost business on top of that, and lost customer trust. A business could also have extensive legal costs associated with a breach.
According to IBM Security’s report, the cost of a data breach climbed again in 2022. The global cost of one breach is now $4.35 million, up 2.6% from last year. If your business is in the U.S., the cost rises to $9.44 million. In Canada, the average data breach costs companies $5.64 million.
Costs for smaller companies tend to be a little lower. But breaches are often more devastating to SMBs. They don’t have the same resources that larger companies do to offset all those costs.
It’s estimated that 60% of small companies go out of business within six months of a cybersecurity breach.
Companies don’t need to resign themselves to the impending doom of a data breach. There are some proven tactics they can take to mitigate the costs. These cybersecurity practices can limit the damage of a cyberattack.
All these findings come from the IBM Security report. They include hard facts on the benefits of bolstering your cybersecurity strategy.
Cybersecurity Tactics to Reduce the Impact of a Breach
Use a Hybrid Cloud Approach
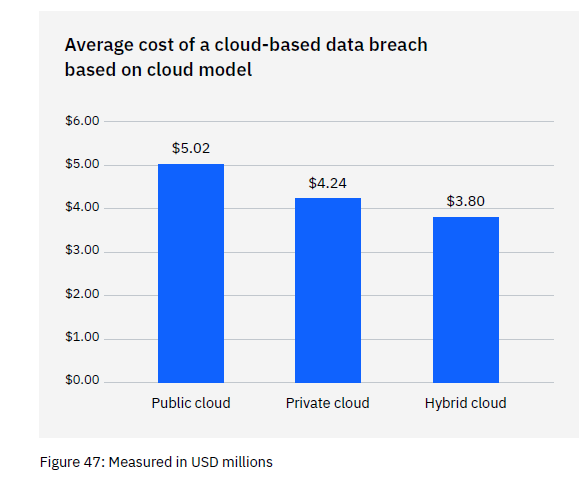
Most organizations use the cloud for data storage and business processes. Researchers found that 45% of all data breaches happen in the cloud. But all cloud strategies are not created equally.
Breaches in the public cloud cost significantly more than those in a hybrid cloud. What is a hybrid cloud? It means that some data and processes are in a public cloud, and some are in a private cloud environment.
What some may find surprising is that using a hybrid cloud approach was also better than a private cloud.
Put in Place an Incident Response Plan & Practice It
You don’t need to be a large enterprise to create an incident response (IR) plan. The IR plan is simply a set of instructions. It’s for employees to follow should any number of cybersecurity incidents occur.
Here is an example. In the case of ransomware, the first step should be disconnecting the infected device. IR plans improve the speed and effectiveness of a response in the face of a security crisis.
Having a practiced incident response plan reduces the cost of a data breach. It lowers it by an average of $2.66 million per incident.
Adopt a Zero Trust Security Approach
Zero trust is a collection of security protocols that work together to fortify a network. An example of a few of these are:
- Multi-factor authentication
- Application safelisting
- Contextual user authentication
Approximately 79% of critical infrastructure organizations haven’t adopted zero trust. Doing so can significantly reduce data breach costs. Organizations that don’t deploy zero trust tactics pay about $1 million more per data breach.
Use Tools with Security AI & Automation
Using the right security tools can make a big difference in the cost incurred during a data breach. Using tools that deploy security AI and automation brought the biggest cost savings.
Data breach expense lowered by 65.2% thanks to security AI and automation solutions. These types of solutions include tools like advanced threat protection (ATP). They can also include applications that hunt out threats and automate the response.
How to Get Started Improving Your Cyber Resilience
Many of these ways to lower data breach costs are simply best practices. You can get started by taking them one at a time and rolling out upgrades to your cybersecurity strategy.
Working with a trusted IT provider, put together a roadmap. Address the “low-hanging fruit” first. Then, move on to longer-term projects.
As an example, “low-hanging fruit” would be putting multi-factor authentication in place. It’s low-cost and easy to put in place. It also significantly reduces the risk of a cloud breach.
A longer-term project might be creating an incident response plan. Then, you would set up a schedule to have your team drill on the plan regularly. During those drills, you could work out any kinks.
Need Help Improving Your Security & Reducing Risk?
Working with a trusted IT partner takes a lot of the security burden off your shoulders. Give us a call today to schedule a chat about a cybersecurity roadmap.
—
Featured Image Credit
This Article has been Republished with Permission from The Technology Press.
by Blog | Feb 28, 2023 | Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity researchers uncovered an alarming mobile statistic. During the first few months of 2022, mobile malware attacks surged by 500%. This is alarming both in scale and because many people aren’t yet protecting smartphones.
For years, mobile phones have become more powerful. They now do many of the same functions as a computer – just with a much smaller screen. Yet, people tend to secure their computers better than they do their smartphones.
This is a behavior that needs to change. Over 60% of digital fraud now occurs through mobile devices. That makes them highly risky if proper safeguards aren’t followed.
Many of these are the same types of protections you have on your computer. It’s time to start thinking about your smartphone as a mini-computer and keeping it just as secure.
Tips to Improve the Security of Your Smartphone
Use Mobile Anti-malware
Yes, your mobile phone needs antivirus/anti-malware too! Malware can and does infect smartphones and tablets. You need to ensure you have a reliable mobile anti-malware app installed.
And beware of those freebies. Freebies are great when you’re talking about food, but not security apps. Malware is often hidden inside free apps. These apps are ironically supposed to make you more secure.
Don’t Download Apps from Unknown Sources
Only download mobile apps from trusted sources. Do not download outside a main app store. Trusted app stores include places like:
- Apple App Store
- Google Play
- The Microsoft Store
- Amazon Appstore
You also should research the app developer online. Make sure they have a good reputation. Once you download a dangerous app to your phone, it can infect it with malware. That malware can remain behind even if you delete the app later.
Don’t Assume Email is Safe
Many people prefer checking email on their phone rather than PC because it’s so handy. But they have a false sense of security about the safety of emails when viewed on a mobile device.
You can’t assume an email is safe just because you’re not on your computer. Be just as wary about unexpected emails and scam emails masquerading as legitimate.
It’s difficult to hover over a link without clicking when on a smartphone. If you see something questionable and want to check the link, open the email on your PC where you can do that.
Beware of SMS Phishing (aka “Smishing”)
In March of 2022, text spam outpaced robocalls. Unwanted text messages rose by 30%, ten percent higher than robocalls. Many of those spam texts are smishing.
Smishing is the text version of phishing. These texts usually contain malicious links. A hacker can potentially breach your device if you click them. The message may also ask you to text back personal information.
Be on the lookout for text messages that don’t quite make sense. For example, getting a shipping notification when you haven’t ordered anything. Also, beware of texts from unknown sources.
Phishing via text message is a growing concern. It’s also one that most people aren’t aware of yet, so they often get caught in its trap.
Remove Old Apps You No Longer User
Approximately 2.6 million apps haven’t had an update in a year or more. Apps are often abandoned by the developer. This can leave security vulnerabilities on your device. Hackers seek out these types of vulnerabilities to exploit. If they aren’t addressed, then they remain a danger.
Go through your device and remove old applications that you are no longer using. There is no reason to keep them around, potentially leaving your device at risk.
Additionally, look at the time of the last update. If it’s over a year, then you may want to consider replacing that app with something more current. App updates often include security-related items. It’s not good when a year or more goes by without the developer making any type of update to the app.
Keep Your Device Updated
Speaking of updates, you also need to keep your device’s operating system updated. Are you using the current version of Android or iOS? Not installing updates can mean your phone has vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities allow hackers to breach your data.
Automate updates as possible. If you have a company with several devices, then it’s a good idea to include your phones on a managed IT services plan.
Use a VPN When on Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi is dangerous. Most people understand that, but many connect to it out of necessity anyhow. You may worry about going over your data plan allotment. Or your mobile carrier reception may be slow. Both cases are reasons people opt to connect to unsecured public hot spots.
You can connect to public Wi-fi with less risk if you use a VPN application. VPNs stand between your device and the internet. They route your data through a secure server. This keeps it away from prying eyes that may be lurking on that public Wi-Fi.
Mobile Security Solutions to Prevent a Data Breach
Don’t wait until your phone is infected with malware to secure it properly. We can help you with automated solutions that protect your device, accounts, and data. Contact us to schedule a consultation.
—
Featured Image Credit
This Article has been Republished with Permission from The Technology Press.
by Blog | Feb 20, 2023 | Cybersecurity
There’s a reason that browsers like Edge have added breached password notifications. Data breaches are an unfortunate part of life. And can have costly consequences for individuals. Hackers can steal identities and compromise bank accounts, just to name a couple.
Cybercriminals breach about 4,800 websites every month with form jacking code. It has become all too common to hear of a large hotel chain or social media company exposing customer data.
Hackers can breach your personal information and passwords without you knowing it. And the time from breach to notification of the breach can be lengthy. One example is the data breach of CafePress. This is a popular online retailer that prints personalized items.
CafePress suffered a data breach in February 2019. That breach exposed millions of names and addresses, security questions, and more. Hackers also breached social security numbers that weren’t encrypted.
As mentioned, the breach happened in February. But many consumers weren’t notified until late summer. The FTC recently took action against the company. This was due to its careless security practices.
The point is that months or years can go by without you knowing about compromised data. Unless you happen to look at the right website, you may not even realize it. Those breached password features in browsers are helpful. But what if you have other information beyond a password compromised?
It’s best to protect yourself with some knowledge. We’ll help by listing several recent breaches. If you’ve interacted with any of these companies, you’ll want to take steps to protect yourself from the fallout.
Recent Breaches of Personal Information That May Impact You
Microsoft Customer Data Breach
On October 19, 2022, Microsoft announced a breach that exposed customer data. A misconfigured server was to blame. The breach exposed certain business transaction data. It’s thought that this breach could have affected more than 65,000 entities worldwide.
2.5 Million Records Exposed in a Student Loan Breach
Did you get a student loan from EdFinancial and the Oklahoma Student Loan Authority (OSLA)? If so, you could be in trouble. The organizations notified impacted individuals by letter in July 2022.
The personal information at risk included:
- Social security numbers
- Email addresses
- Home addresses
- Phone numbers.
The breach compromised the data of over 2.5 million loan recipients.
U-Haul Data Breach of 2.2 Million Individuals’ Data
Large rental firm U-Haul is a household name. It also just had a major data breach. It notified clients in August of 2022 of a compromise of some rental contracts. The contacts in question were between November 5, 2021, and April 5, 2022.
The breach exposed names, driver’s license numbers, and state identification numbers. It affected over 2.2 million individuals that rented vehicles from the company.
Neopets Breach May Have Compromised 69 Million Accounts
You wouldn’t suspect a cute site like Neopets to be a cybersecurity risk. But users of the platform got a rude awakening due to a breach of the service. An estimated 69 million accounts may have had emails and passwords leaked.
The full stolen Neopet database and copy of the source code were being offered for sale for about $94,500.
One Employee Computer Causes a Marriott Breach
Hotel giant Marriott suffered another breach in July 2022. It blamed a single unsecured employee computer. About 300-400 individuals had data leaked. This data included credit card numbers and other confidential information.
Unfortunately, the company shows a pattern of poor cybersecurity. Within the last four years, it has suffered three separate breaches. That’s enough to want to pay in cash or use a pre-paid card if you stay there.
Shield Health Care Group Exposes Up to 2 Million Records
In March of 2022, Shield Health Care Group detected a breach. This Massachusetts-based company found that hackers breached up to 2 million customer records. This includes medical records, social security numbers, and other sensitive personal data.
Flagstar Bank Takes 6 Months to Identify Individuals Affected in a Breach
In December of 2021, Flagstar Bank suffered a breach. It wasn’t until 6 months later that it identified the individuals affected. And the impact was large. It included exposed social security numbers. The hack impacted about 1.5 million customers.
8.2 million Current and Former Customers of Block Compromised
Block was formerly known as Square, a popular payment processing platform. It announced in April of 2022 that it was breached the previous December. A former employee accessed customer names and brokerage account numbers. Some accounts also had other stock trading information accessed.
About 8.2 million current and former customers had their data exposed.
Crypto.com Breach Nets Hackers Over $30 Million
Cryptocurrency may be hot at the moment, but it’s very susceptible to cyberattacks. In January 2022, over 483 users had their Crypto.com wallets breached.
The criminals made it past two-factor authentication, which is usually quite effective. They stole about $18 million in bitcoin and $15 million in Ethereum and other cryptocurrencies.
How Secure Are Your Passwords?
There are many solutions that can help you better manage and secure your passwords. Give us a call to learn more about protecting your personal data from a breach.
—
Featured Image Credit
This Article has been Republished with Permission from The Technology Press.
by Blog | Feb 15, 2023 | Cybersecurity
Data privacy has been a growing requirement ever since the internet age began. So much personal information is flying around through computer networks. Protecting it has become a mandate.
Most companies must follow HIPAA, GDPR, or another industry or locality-based privacy rule. By the end of 2024, 75% of the world’s population will have their personal data protected. It will fall under one or more privacy regulations.
You don’t need to be a large enterprise organization to have data privacy compliance at the top of your mind. It goes hand in hand with cybersecurity. Additionally, privacy requirements hit all sized companies.
Between July 2020 and July 2021, GDPR violations rose by 113.5%. The number of associated fines also jumped, by 124.92%. When it comes to HIPAA violations, each incident can carry a penalty between $100 to $25,000.
It’s important to make data privacy a priority and factor it into all your data collection processes. When companies collect, send, or store personally identifiable information (PII) it needs protection. This means putting adequate safeguards in place.
To stay on top of your privacy compliance obligations, you should also keep up with trends in this area. Next up, we’ve documented the biggest data privacy trends happening in 2023 that you should be aware of.
What’s Happening in Data Privacy Compliance?
AI Governance
Approximately 40% of privacy compliance technology needs artificial intelligence (AI) to operate. AI has certainly made its way into many of the applications we use on a daily basis.
When you’re typing in MS Word and text just springs up as a suggestion, that’s AI predicting what you’ll type next. When working on a photograph in Photoshop, you can now click a button to give a frowning face a smile. This is also the work of AI.
So, it’s no surprise that AI is running many of the algorithms responsible for keeping data protected. But what happens when there is a problem with the AI?
This is the question that AI governance is working to address. This is a new trend in data privacy because AI has never been so prevalent throughout the data journey as it is now.
Whenever AI is used in the data protection area, organizations need to govern it properly. This helps ensure that automated processes aren’t accidentally exposing sensitive data.
Consumer Privacy UX
A trend that we’ve seen over the last several months is putting more privacy power into the consumer’s hands. Many privacy regulations require that apps and websites provide data transparency. They need to tell people what data they’re collecting, how they’re collecting it, and what they do with it. People also need an “out” to get their data back.
These needs have led to consumer privacy UX becoming a “thing.” You can think of this as a centralized privacy portal. A place people can access privacy-related settings in various apps. This gives better visibility into how their data is being used.
Increased Scrutiny of Remote Employee Monitoring
The pandemic has forever changed the global workforce. Many organizations are now running completely remote offices. Or may be using a mix of remote and in-office staff. The dramatic increase in people working from home has led to data collection changes. Companies are ramping up their monitoring of those employees working off-site.
But this type of monitoring opens a can of worms when it comes to data privacy. Organizations need to ensure that they aren’t encroaching on the rights of their staff. This is most pertinent when putting monitoring in place on employee devices.
For example, approximately 49% of remote employees use their personal computers for work. Companies often put endpoint device monitoring in place for security reasons. They need to ensure they are not gathering or backing up any personal data. That would be data owned by the employee and not the company.
Data Localization
One of the concerns when the social app TikTok became popular relates to location. With the firm being a China-based company, people worried about the privacy of their data. The data was originally stored on servers governed by the Chinese government. A country with very different data privacy rules than the US and other countries.
Data localization is going to become more prevalent. Increasingly organizations look at where their cloud data is being stored. Where a server resides governs the privacy rules and regulations that it may fall under. Thus, companies and governments are now asking a question of cloud providers. This is, “Where is my data stored?” Many want their data to be as close to home as possible.
Privacy-Enhancing Computation (PEC)
Data privacy by design is a fairly new term. Using privacy-enhancing computation is a way that AI is helping cybersecurity. By using PEC as a built-in component of software and apps, developers provide value to clients. They address privacy concerns by making data protection more automated.
Look for PEC components in data analytics when shopping for business tools.
When Is the Last Time You Had a Compliance Check?
How are your data privacy protections? Are you risking a penalty due to lax controls? Give us a call! We can help with a compliance checkup.
—
Featured Image Credit
This Article has been Republished with Permission from The Technology Press.
by Blog | Feb 10, 2023 | Cybersecurity, IT Management
Our technology inevitably comes with us when we travel. Most of us won’t even travel to the end of the block without our smartphones. When you go on a trip, not having your technology there when you need it can ruin your day.
Travel smarter and more securely by doing several checks before you go. Use our handy tech travel checklist. It can save you from suffering from lost devices, missing chargers, or a data breach.
1. Check Your Apps
Have you ever sat at an airport gate wondering why it looked so empty? You then found out that your gate had changed, and you had no idea. You go rushing to the other end of the concourse, hoping you’re not too late.
How did everyone else know about the gate change? They most likely had the app for the airline and received a notification.
Before you leave for a trip, make sure to download any apps you may need. It’s better to download them when you’re at home on your own Wi-Fi. If you wait until you’re at the airport, reception may be an issue.
Some of the apps you may want to grab or update before your trip are:
- Airline app
- Train app
- Hotel app
- Theme park app
- Camping ground app
- Weather app
- City tourism app
2. Check Your Cords & Adapters
People leave behind countless chargers and adapters every day. They litter airports, restaurants, and train stations around the world. Make sure to bring a backup charger for your laptop, tablet, or phone. Otherwise, you may find yourself paying a premium for a new charger in a gift shop. Your device could also go black if you lose its charger and can’t quickly get a new one.
3. Check Your Power
A great way to ensure you have the power you need is to buy a small charging battery. You can find these in most major retailers or online. They are small “blocks” that hold a charge and can power up a cell phone in a pinch.
Having this extra backup also helps you avoid potential juice-jacking ports. These are fake or compromised public USB charging ports. Hackers use them to steal your data when you plug in.
4. Check Your Mobile Plan
If you’re traveling out of the country, you’ll want to check your mobile plan. If you don’t have the ability to call internationally, then you may not be able to text or call home.
Carriers can add an international capability to your plan, but ask about pricing. It can get expensive if you’re on long calls or using mobile data. An alternative is to set up a VoIP app you can use with your office, friends, or family while you’re traveling. These enable both calls and SMS, but you do need an internet connection.
5. Check or Add a VPN
Free Wi-Fi may be a welcome site when you’re on the road, but it can also be dangerous. You don’t know who else is using that Wi-Fi. A hacker hanging out on the connection can easily steal your data if you’re not protected.
It’s better to use either your mobile carrier connection or a virtual private network (VPN) app. VPN plans are inexpensive and will keep your data encrypted, even if you’re on public Wi-Fi.
6. Check Your Backup
Unfortunately, mishaps occur when traveling. You may leave your phone behind on a boat, have your luggage lost, or get your device stolen while in a crowded area.
10% of all laptop thefts happen in airports.
Don’t lose all your data with the device! Back up your devices to the cloud or local storage before you travel. This ensures that you won’t lose the valuable information on your device. You also won’t need to think twice about enacting a remote “wipe my device” command if necessary.
7. Check Your Device Security
Make your devices as secure as possible before you hit the road. When we’re traveling, our minds are occupied by other things. So, you may not think to check your antivirus or avoid suspicious phishing links.
Protect your devices before you go using:
- Antivirus/anti-malware
- DNS filtering
- Screen lock with passcode
- Sharing features turned off
- VPN application
- Find-My-Device feature turned on
8. Check Your Double-Checks
What do we mean by checking your double-checks? Use the buddy system as a backup. When the family is getting off a plane, each should check with the other that they have all their devices.
If you’re traveling alone, have a friend or family member check up by text. Did you grab your charger? Is your VPN turned on?
Those little reminders can go a long way toward avoiding digital travel nightmares.
Improve the Security of Your Devices Now
Don’t leave your devices unprotected. This could mean a breach of your banking app or personal data. Contact us for device security solutions to reduce your risk.
—
Featured Image Credit
This Article has been Republished with Permission from The Technology Press.
by Blog | Jan 31, 2023 | Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity insurance is still a pretty new concept for many SMBs. It was initially introduced in the 1990s to provide coverage for large enterprises. It covered things like data processing errors and online media.
Since that time, the policies for this type of liability coverage have changed. Today’s cyber insurance policies cover the typical costs of a data breach. Including remediating a malware infection or compromised account.
Cybersecurity insurance policies will cover the costs for things like:
- Recovering compromised data
- Repairing computer systems
- Notifying customers about a data breach
- Providing personal identity monitoring
- IT forensics to investigate the breach
- Legal expenses
- Ransomware payments
Data breach volume and costs continue to rise. 2021 set a record for the most recorded data breaches on record. And in the first quarter of 2022, breaches were up 14% over the prior year.
No one is safe. Even small businesses find they are targets. They often have more to lose than larger enterprises as well. About 60% of small businesses close down within 6 months of a cyber incident.
The increase in online danger and rising costs of a breach have led to changes in this type of insurance. The cybersecurity insurance industry is ever evolving. Businesses need to keep up with these trends to ensure they can stay protected.
Here are some of the cyber liability insurance trends you need to know about.
Demand is Going Up
The average cost of a data breach is currently $4.35 million (global average). In the U.S., it’s more than double that, at $9.44 million. As these costs continue to balloon, so does the demand for cybersecurity insurance.
Companies of all types are realizing that cyber insurance is critical. It’s as important as their business liability insurance. Without that protection, they can easily go under in the case of a single data breach.
With demand increasing, look for more availability of cybersecurity insurance. This also means more policy options, which is good for those seeking coverage.
Premiums are Increasing
With the increase in cyberattacks has come an increase in insurance payouts. Insurance companies are increasing premiums to keep up. In 2021, cyber insurance premiums rose by a staggering 74%.
The costs from lawsuits, ransomware payouts, and other remediation have driven this increase. Insurance carriers aren’t willing to lose money on cybersecurity policies. Thus, those policies are getting more expensive. This is at the same time as they are more necessary.
Certain Coverages are Being Dropped
Certain types of coverage are getting more difficult to find. For example, some insurance carriers are dropping coverage for “nation-state” attacks. These are attacks that come from a government.
Many governments have ties to known hacking groups. So, a ransomware attack that hits consumers and businesses can very well be in this category.
In 2021, 21% of nation-state attacks targeted consumers, and 79% targeted enterprises. So, if you see that an insurance policy excludes these types of attacks, be very wary.
Another type of attack payout that is being dropped from some policies is ransomware. Between Q1 and Q2 of 2022, ransomware attacks increased by 24%.
Insurance carriers are tired of unsecured clients relying on them to pay the ransom. So many are excluding ransomware payouts from policies. This puts a bigger burden on organizations. They need to ensure their backup and recovery strategy is well planned.
It’s Harder to Qualify
Just because you want cybersecurity insurance, doesn’t mean you’ll qualify for it. Qualifications are becoming stiffer. Insurance carriers aren’t willing to take chances. Especially on companies with poor cyber hygiene.
Some of the factors that insurance carriers look at include:
- Network security
- Use of things like multi-factor authentication
- BYOD and device security policies
- Advanced threat protection
- Automated security processes
- Backup and recovery strategy
- Administrative access to systems
- Anti-phishing tactics
- Employee security training
You’ll often need to fill out a lengthy questionnaire when applying for insurance. This includes several questions about your cybersecurity situation. It’s a good idea to have your IT provider help you with this.
This can seem like a lot of work that you have to do to qualify for cyber insurance. As you review the questions, your IT partner can identify security enhancements. Just like other forms of insurance, if you take steps to reduce risk, it can often reduce your premiums.
So, it pays to do a cybersecurity review before applying for cyber insurance. You can save yourself time and money. It can also fortify your defenses against cyberattacks.
Need Help Making Sense of Cybersecurity Policies?
Cybersecurity coverage and insurance applications can be complex. If you answer wrong on a question, it can mean paying hundreds more in premiums than you should.
If you’re considering cybersecurity insurance, don’t go it alone. Give us a call and schedule a consultation. We can explain the policy details and provide guidance.
—
Featured Image Credit
This Article has been Republished with Permission from The Technology Press.